The documentation you are viewing is for Dapr v1.14 which is an older version of Dapr. For up-to-date documentation, see the latest version.
Deploy Dapr per-node or per-cluster with Dapr Shared
Dapr automatically injects a sidecar to enable the Dapr APIs for your applications for the best availability and reliability.
Dapr Shared enables two alternative deployment strategies to create Dapr applications using a Kubernetes Daemonset for a per-node deployment or a Deployment for a per-cluster deployment.
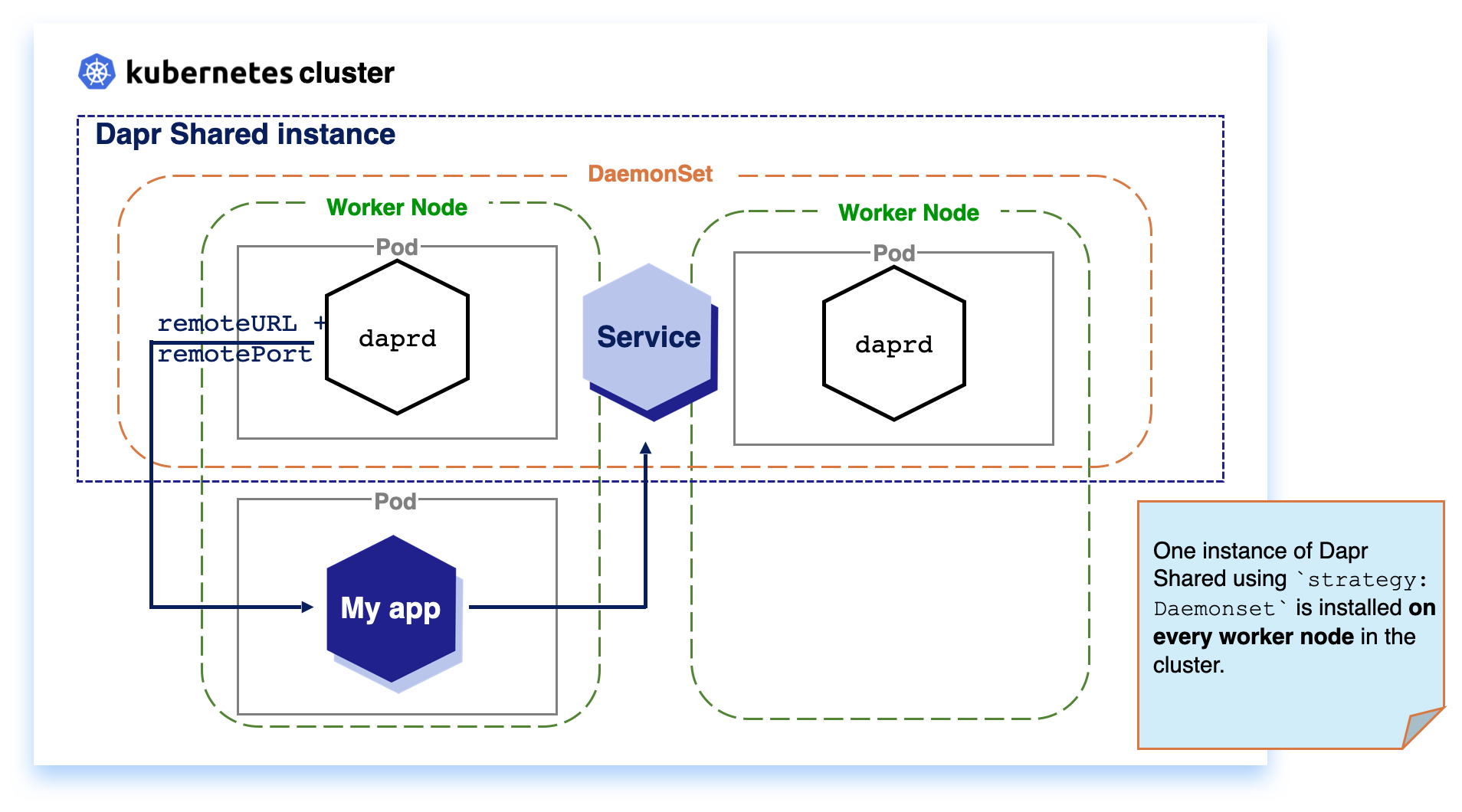
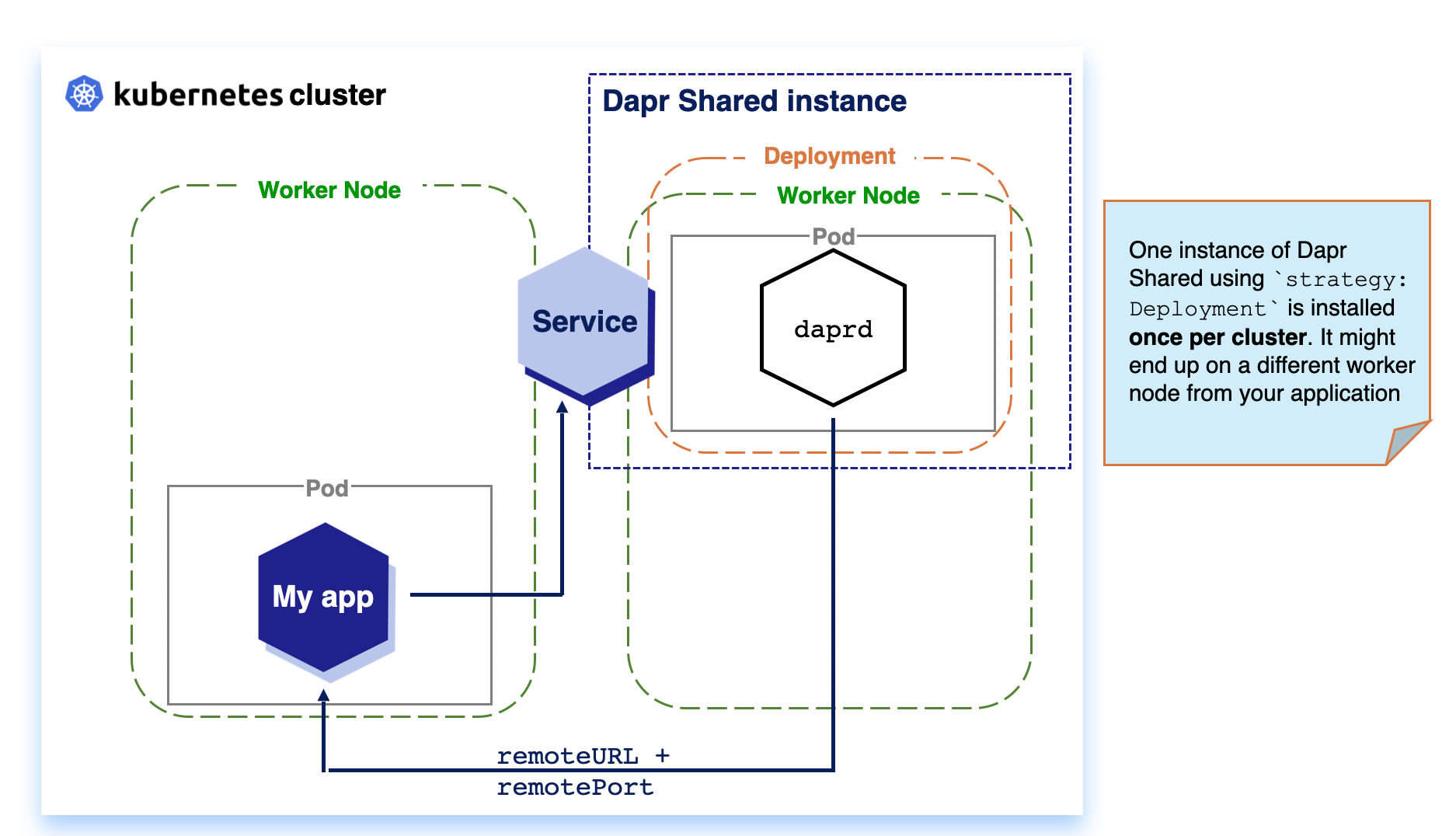
DaemonSet: When running Dapr Shared as a KubernetesDaemonSetresource, the daprd container runs on each Kubernetes node in the cluster. This can reduce network hops between the applications and Dapr.Deployment: When running Dapr Shared as a KubernetesDeployment, the Kubernetes scheduler decides on which single node in the cluster the daprd container instance runs.
Dapr Shared deployments
For each Dapr application you deploy, you need to deploy the Dapr Shared Helm chart using differentshared.appIds.
Why Dapr Shared?
By default, when Dapr is installed into a Kubernetes cluster, the Dapr control plane injects Dapr as a sidecar to applications annotated with Dapr annotations ( dapr.io/enabled: "true"). Sidecars offer many advantages, including improved resiliency, since there is an instance per application and all communication between the application and the sidecar happens without involving the network.
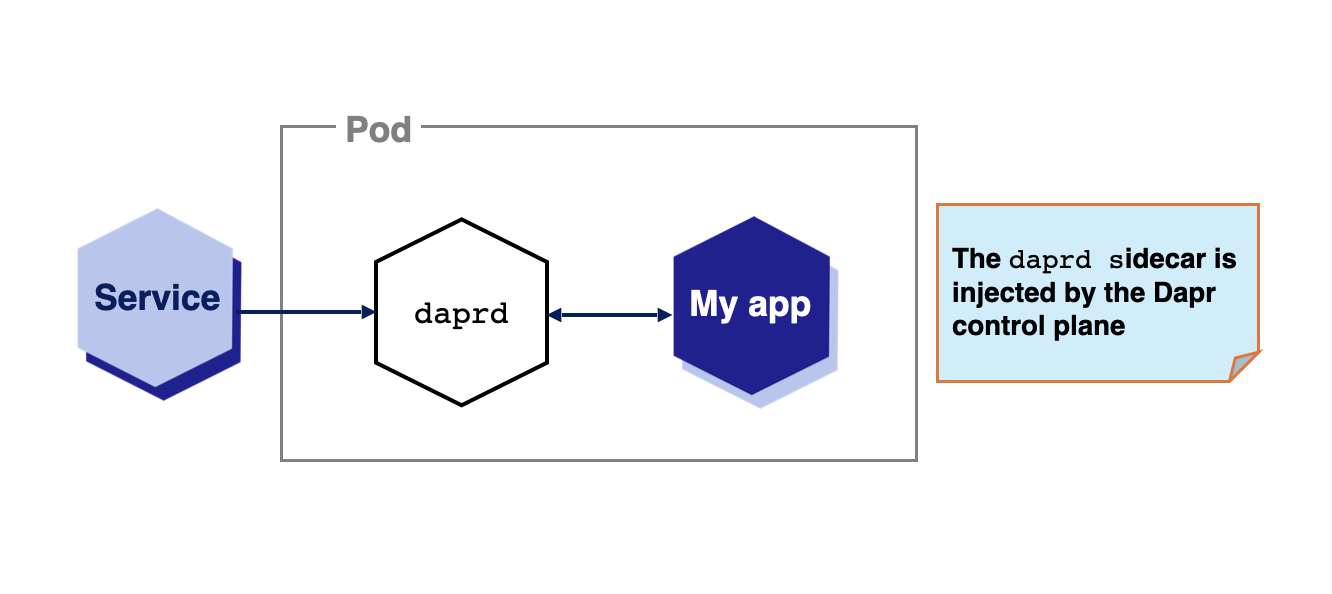
While sidecars are Dapr’s default deployment, some use cases require other approaches. Let’s say you want to decouple the lifecycle of your workloads from the Dapr APIs. A typical example of this is functions, or function-as-a-service runtimes, which might automatically downscale your idle workloads to free up resources. For such cases, keeping the Dapr APIs and all the Dapr async functionalities (such as subscriptions) separate might be required.
Dapr Shared was created for these scenarios, extending the Dapr sidecar model with two new deployment approaches: DaemonSet (per-node) and Deployment (per-cluster).
Important
No matter which deployment approach you choose, it is important to understand that in most use cases, you have one instance of Dapr Shared (Helm release) per service (app-id). This means that if you have an application composed of three microservices, each service is recommended to have its own Dapr Shared instance. You can see this in action by trying the Hello Kubernetes with Dapr Shared tutorial.DeamonSet(Per-node)
With Kubernetes DaemonSet, you can define applications that need to be deployed once per node in the cluster. This enables applications that are running on the same node to communicate with local Dapr APIs, no matter where the Kubernetes Scheduler schedules your workload.
Note
SinceDaemonSet installs one instance per node, it consumes more resources in your cluster, compared to Deployment for a per cluster deployment, with the advantage of improved resiliency.
Deployment (Per-cluster)
Kubernetes Deployments are installed once per cluster. Based on available resources, the Kubernetes Scheduler decides on which node the workload is scheduled. For Dapr Shared, this means that your workload and the Dapr instance might be located on separate nodes, which can introduce considerable network latency with the trade-off of reduce resource usage.
Getting Started with Dapr Shared
Prerequisites
Before installing Dapr Shared, make ensure you have Dapr installed in your cluster.If you want to get started with Dapr Shared, you can create a new Dapr Shared instance by installing the official Helm Chart:
helm install my-shared-instance oci://registry-1.docker.io/daprio/dapr-shared-chart --set shared.appId=<DAPR_APP_ID> --set shared.remoteURL=<REMOTE_URL> --set shared.remotePort=<REMOTE_PORT> --set shared.strategy=deployment
Your Dapr-enabled applications can now make use of the Dapr Shared instance by pointing the Dapr SDKs to or sending requests to the my-shared-instance-dapr Kubernetes service exposed by the Dapr Shared instance.
The
my-shared-instanceabove is the Helm Chart release name.
If you are using the Dapr SDKs, you can set the following environment variables for your application to connect to the Dapr Shared instance (in this case, running on the default namespace):
env:
- name: DAPR_HTTP_ENDPOINT
value: http://my-shared-instance-dapr.default.svc.cluster.local:3500
- name: DAPR_GRPC_ENDPOINT
value: http://my-shared-instance-dapr.default.svc.cluster.local:50001
If you are not using the SDKs, you can send HTTP or gRPC requests to those endpoints.
Next steps
- Try the Hello Kubernetes tutorial with Dapr Shared.
- Read more in the Dapr Shared repo
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Glad to hear it! Please tell us how we can improve.
Sorry to hear that. Please tell us how we can improve.